Caching slow queries (IMDB)
Prerequisites
- A Readyset instance connected to a MySQL or Postgres database with Grafana (we recommend that you use the Readyset Demo to set this up)
- MySQL or Postgres client, depending on the primary database
Steps
1. Download the IMDB dataset & load it into your database
First, download the IMDB dataset for MySQL:
curl -L -O "https://readyset.io/quickstart/imdb-mysql.sql"Then, connect to your Readyset instance and import the dataset:
mysql -h<Readyset URL> -U<username> -P<port number> <database name> -p<password> < imdb-mysql.sqlNote: If you used the Readyset Demo instructions to set up Readyset (recommended), you can use the following command to connect:
mysql -h127.0.0.1 -uroot -P3307 testdb -preadyset < imdb-mysql.sql2. Connect to Readyset & make sure the tables have been imported
It could take a few seconds for Readyset to import the tables. You can check whether they've been successfully imported by connecting to Readyset through your database client and running:
SHOW READYSET TABLES;Once the table is imported, you will see that the status of that table is 'snapshotted'.
3. Run a query against your primary database
Once the tables have been imported into Readyset, we can start running queries.
Let's try this one, which counts how many titles released in 2000 had an average rating that was higher than 5:
SELECT count(*) FROM title_ratings
JOIN title_basics ON title_ratings.tconst = title_basics.tconst
WHERE title_basics.startyear = 2000 AND title_ratings.averagerating > 5;By default, this query is proxied to the primary database.
4. Cache the query in Readyset
We can cache it in Readyset by running the following:
CREATE CACHE FROM SELECT count(*) FROM title_ratings
JOIN title_basics ON title_ratings.tconst = title_basics.tconst
WHERE title_basics.startyear = 2000 AND title_ratings.averagerating > 5;We can check the Grafana dashboard to see that the query was successfully cached, and compare latencies.
Note: if you set up Readyset via the Readyset Demo instructions (recommended), then you can open Grafana by going to localhost:4000 in your browser.
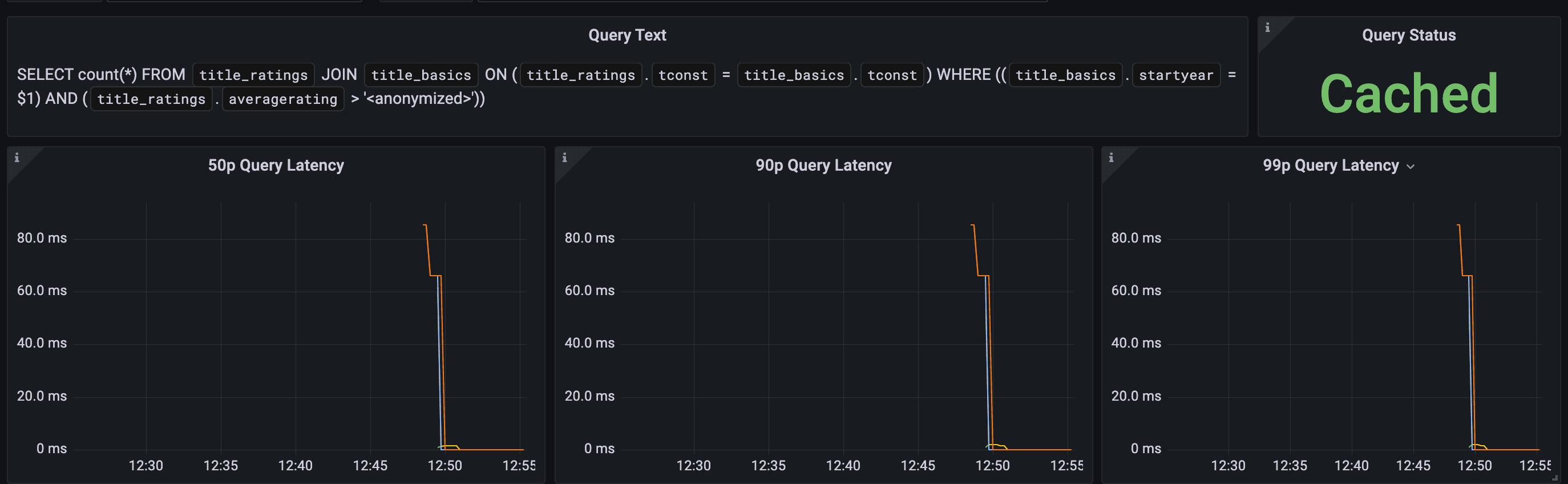
Here, we can see that the 99th percentile latencies for this query fell from over 80ms against Postgres to < 1ms against Readyset. Huzzah!